JavaScript Basics
Variables
Variable Names
- a variable name must begin with a letter, underscore (
_), or dollar sign ($) - and they cannot use hyphens
- they cannot begin with numbers, although they may be used subsequently, e.g.
variable1 - JavaScript is case sensitive
The convention around naming variables is to use camelCase
var theStarterLeague = 125;
var food_truck = "Coffee";
var mixtape01 = true;
var vinyl = ['Miles Davis', 'Frank Sinatra', 'Ray Charles'];
Values
Primitives
-
String
-
Number
-
Boolean (
trueorfalse) -
undefined -
null
Objects
- Array
- Object
- Date
- Function
- Symbol
- Promise
typeof variable == undefined
Array.isArray(variable)
Strict mode
"use strict"
// better error checking in this scope
Statements
JavaScript is a set of statements, executed by the browser in the sequence they are written
log(polaroid);
return('bicycle lane');
alert('Congratulations, you ' + outcome);
Debugging
Pause the flow of JavaScript
alert()prompt()confirm()
Browser console
console.log("Hello console!");
// provide labels for variables
console.log({ var1, var2 })
// style console log
console.log("%c Hello beautiful console", "color: pink; font-weight: bold; background-color: black;")
console.table(array);
console.table([ var1, var2 ])
console.assert(condition, "condition is false")
console.error("Error!");
console.group("group label")
console.groupCollapsed("group label")
...
console.groupEnd()
console.dir(object)
console.dir(domNode)
console.count(label)
console.time()
console.timeLog()
console.trace()
Control flow
Comparison
a == b– same valuea === b– same value and same typea = b– declaration, not a comparison!
Loops
For-loop
for (let i=0; i<10; i++) {
// ...
}
For-loop over property names (i.e. indices) of an iterable (e.g. array)
for (let i in arr) {
console.log(i);
}
For loop over property values (i.e. array items) of an iterable (e.g. array)
for (let i of arr) {
console.log(i);
}
For loop over indices and property values
for (let [i, item] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(i, item);
}
While-loop
let i = 5
while (i < 10) {
i++;
}
Conditionals
if (isTasty) {
} else if (isEatable) {
} else {
}
Shorthand
const greeting = isNice ? "Hello! Nice to see you." : "Hi.";
Switch
switch (food) {
case "Broccoli":
console.log("Nice!");
break;
case "Carrot":
console.log("Awesome!!");
break;
default:
break;
}
Try catch
try {
} catch {
}
Numbers
const division = 16 / 0;
isNaN(division);
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER
Math.random() // float in [0, 1)
const random = Math.floor(1000 * Math.random()) // integer from 0 ... 999
Round to two decimal places
parseFloat(e.offsetX).toFixed(2)
Strings
let helloString = "Hello World"
const sentence = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."
// CREATE
// template string
const string = `My name is ${firstName}`
// Substring
string.substring(indexStart, indexEnd)
string.substring(1) // "ello World"
string.substring(0,4)
string.substr(start, length)
string.substr(0, 4)
// String contains/includes Substring
sentence.includes("dog")
// pad start/end
let str = '12'
str.padStart(3, '0') // 012
str.padEnd(3, '0') // 120
// Split
const pathArray = sentence.split(' ')
sentence.split(/[,;|!?]/)
// Find and replace with RegEx
const otherSentence = sentence.replace(/the/g, "a")
sentence.replaceAll("i", "ii")
Letter from number
const character = String.fromCharCode(97 + n);
const string = String.fromCharCode(97+0, 97+7, 97+16);
const A = 'A'.charCodeAt(0);
let numberToCharacter = number => String.fromCharCode(A + number);
let characterToNumber = character => character.charCodeAt(0) - A;
Regular Expression
const matches = /.+\s.+/g.test("asffdsg dsgsdg")
string.match(/[0-9]/);
Tagged Template
custom`My name is ${firstName}`
function custom(stringsArray, ...values) {
console.log(stringsArray, values)
}
bold`My name is ${firstName}`
function bold(strings, ...values) {
return values.reduce((finalString, value, index) => {
return `${finalString}<strong>${value}</strong>${strings[index + 1]}`
}, strings[0])
}
Arrays
let numbers = [5, 10, 15, 1, 2]
const abc = ["a", "b", "c", "a", "e"]
Array.from({ length: 5 }) // [0,1,2,3,4]
Array.from(Array(5)) // [0,1,2,3,4]
Array.from({ length: 5 }, (element, index) => index + 1) // [1,2,3,4,5]
// array from HTMLCollection
Array.from(document.getElementsByClassName('async-image'))
Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('.async-image'))
numbers.fill(1) // [1,1,1,1,1]
// Get array length
numbers.length // 3
// Get array element at index
numbers[2] // 15
numbers.at(1) // 10
// includes
numbers.includes(2)
// index of
let list = [0,5,10,15]
const index = list.indexOf(5)
// array contains object
const fruits = ["apple", "pear", "orange"]
if (fruits.indexOf("apple") > -1) console.log("fruits contains apple")
// last index of
abc.lastIndexOf("a")
// start offset
"abcabc".indexOf("a") // 0
"abcabc".lastIndexOf("c") // 5
"abcabc".indexOf("a", 2) // 3
"abcabc".lastIndexOf("c",4) // 2
// ADD
// add a new element to an array (at the end)
numbers.push(7)
// add a new element to an array (at the beginning)
numbers.unshift(2)
// concatenate
let numbers1 = [1,2];
let numbers2 = [3,4];
let numbers = numbers1.concat(numbers2) // [1,2,3,4]
// DELETE
// delete element at the end
numbers.pop()
// delete element at the beginning
numbers.shift()
// delete element at index
delete numbers[0] // numbers[0] = undefined
// array to String
numbers.toString()
numbers.join(" - ")
// sort array
numbers.reverse()
numbers.sort()
numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b)
spliceand slice
numbers.splice(spliceIndex, spliceRangeOverwrite, newArrayItems ...);
let numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8];
numbers.splice(3,0, 20,25); // adds 20 and 25 to numbers at index 3
numbers.splice(0,2); // removes the first two elements
numbers.splice(2,0, "0", "1"); //
const removedItemAtIndex2 = numbers.splice(2,1)
numbers.slice(sliceBeginIndex, sliceEndIndex=array.length);
numbers.slice(3); // subarray from index 3 upwards
numbers.slice(0,2); // array with the first two elements
numbers.slice(1,4)
Array methods
const numbers = [4, -3, 9, 16, 25]
const persons = [
{ name: "John", age: 72 },
{ name: "Sally", age: 35 },
{ name: "Lisa", age: 15 },
]
// for each
numbers.forEach((item, i) => console.log(item, i))
numbers.find(item => item > 2)
numbers.findIndex(item => item === 2)
numbers.every(item => item > 0) // true if every item meets criterion
numbers.some(item => item > 0) // true if at least one item meets criterion
// map
numbers.map(Math.sqrt)
numbers.map(item => item*2)
persons.map(person => person.age)
// general
array.map((currentItem, index, arrayObject) => {}, thisBoundValue)
// filter
numbers.filter(value => value >= 0) // positive numbers
numbers.filter((value, index, array) => value >= 0)
// general
array.filter((elem, i, rep) => {})
// reduce
numbers.reduce((sum, number) => sum + number, 0)
const array = [1, 2, 3, [40, 50]]
// flatten array
array.flat()
array.flat(2)
array.flat(Infinity)
// flatMap => more performant than .map().flat()
array.flatMap((currentValue, index, array) => { /* … */ } )
get last item from array
const lastItem = array[array.length - 1]; // slowest
const lastItem = array.slice(-1);
const lastItem = array.pop(); // fastest, but mutates the array!
Array polyfill
Array.prototype.myForEach = function(callback){
for(let i = 0; i < this.length; i++){
callback(this[i], i, this);
}
}
Dates
let date = new Date() // current date and time
new Date(year, month, day, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds)
new Date(year, month)
new Date(milliseconds)
new Date("2017-06-23")
new Date("2017")
new Date("2017-06-23T12:00:00-09:45")
new Date("June 23 2017")
new Date("Jun 23 2017 07:45:00 GMT+0530")
date.getDay() // 1-31
date.getDay() // 0-6
date.getFullYear() // (yyyy)
date.getHours() // 0-23
date.getMilliseconds() // 0-999
date.getMinutes() // 0-59
date.getMonth() // 0-11
date.getSeconds() // 0-59
date.getTime() // milliseconds since 1970
Functions
function sayHello(name) {
return('Hello ' + name);
};
sayHello('Markus');
Arguments
function myFunction(title, name, ...) {
console.log(arguments[1]) // "Markus"
};
myFunction("MSc", 'Markus', 15);
Functional programming
function Planet(mass, radius) {
this.mass = mass
this.radius = radius
}
const planet = Planet(10, 3)
Arrow notation
() => {
// function content
}
( properties ) => {
// function content
}
Immediately invoked function expression
(function() {
console.log("IIFE!")
})();
Callback function
setTimeout(callback, 1000);
function callback() {
}
Workaround: Named parameters
Pass objects to function calls (using object destructuring)
perform({ oneRequired: "Yes!", threeOptional: true })
function perform({ oneRequired, twoOptional = null, threeOptional = false } = {}) {
// ...
}
Generator function
Generator function denoted by * after function keyword
function* idGenerator() {
let id = 1
while (true) {
yield id
id++
}
}
const generator = idGenerator()
const id1 = generator.next()
const id2 = generator.next()
bind, call, apply
let a = { name: "A" }
let b = { name: "B" }
function speak(arg) { console.log(this.name, arg) }
speak.bind(b)()
speak.bind(b)("argument")
speak.bind(b, "argument").call()
speak.bind(b).call("argument", ...)
speak.apply(a)
JavaScript Event Loop
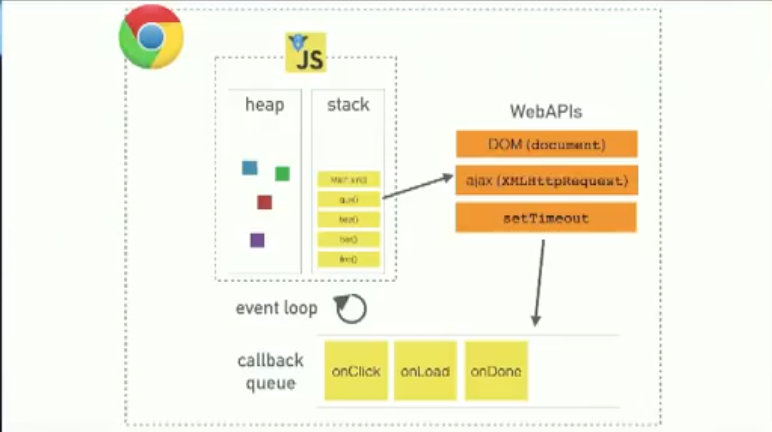
Call Stack
single threaded = single callstack = one thing at a time
Web APIs
pushed to task queue when done
Callback/Task Queue
Event Loop
If stack is empty, task pending in the task queue is pushed onto the stack.
Objects | Object Literal
- objects = collection of key and value pairs
- keys = properties
- values
var school = {
name: 'The Starter League',
location: 'Merchandise Mart',
students: 120,
teachers: ['Jeff', 'Raghu', 'Carolyn', 'Shay'],
calculate: (input) => input**2
}
const object = {
title: "The Old Man and the Sea",
author: "Earnest Hemingway",
year: "1952",
getSummary: function() {
return `${this.title} was written by ${this.author} in ${this.year}`;
}
}
const person = { name: "Max", age: 25 }
// Create object via `new`
wordData = new Object()
// get all property keys and values (as arrays)
Object.keys(myObject)
Object.values(myObject)
// check if key exists
if (person.name) { }
if ("key" in object) { }
if (object.hasOwnProperty('key')) { }
// access property
school['name']
school.name
// set property
school.name = "High School"
school.age = 350 // new property
// shorthand deriving property name and value
const name = 'ello'
const age = 5
const oj = { name, age }
// dynamic property name
const propertyName = 'superpower';
const woman = { [propertyName]: 'everything' } // setting
woman[propertyName] // getting
//
object = { age: 5 }
Object.defineProperty(object, "name", {
writable: false,
value: undefined,
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
get() { return this.name },
set(newValue) { this.name = newValue }
})
// 2-way data binding for input element
const inputElement = document.querySelector("input")
const inputObject = {}
Object.defineProperty(inputObject, "name", {
get() {
return inputElement.value
},
set(newValue) {
inputElement.value = newValue
}
})
Objects | Function definition
Constructor
Example 1
function Book(title, author, year) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.year = year;
this.getSummary = function() {
return `${this.title} was written by ${this.author} in ${this.year}`;
}
}
// Instantiate an Object
const book = new Book("The Old Man and the Sea", "Earnest Hemingway", "1952");
Example 2
function Circle(x,y,r) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.r = r;
this.draw = function () {
// draw
}
}
let circle = new Circle(10,20, 5);
circle.draw();
Prototype
function Book(title, author, year) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.year = year;
}
Book.prototype.getSummary = function() {
return `${this.title} was written by ${this.author} in ${this.year}`;
}
Book.prototype.revise = function(newYear) {
this.year = newYear;
this.revised = true;
}
Inheritance
function Lexicon(title, author, year, partNumber) {
Book.call(this, title, author, year);
this.partNumber = partNumber;
}
// Inherit Prototype
Magazine.prototype = Object.create(Book.prototype);
// Use Lexicon Constructor
Lexicon.prototype.constructor = Lexicon;
const lexicon3 = new Lexicon("Mammals", "Charles Darwin", "1940", "3");
Object Create
// Object of prototype functions
const bookProtos = {
this.getSummary: function() {
return `${this.title} was written by ${this.author} in ${this.year}`;
},
this.revise = function(newYear) {
this.year = newYear;
this.revised = true;
}
}
// Create object
const book = Object.create(bookProtos);
book.title = "The Old Man and the Sea";
book.author = "Earnest Hemingway";
book.year = "1952";
// Create object
const book2 = Object.create(bookProtos, {
title: { value: "The Old Man and the Sea" },
author: { value: "Earnest Hemingway" },
year: { value: "1952" }
});
Classes (ES6+)
class Book {
constructor(title, author, year) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.year = year;
}
getSummary() {
return `${this.title} was written by ${this.author} in ${this.year}`;
}
revise(newYear) {
this.year = newYear;
this.revised = true;
}
static topBookStore() {
return "Barnes & Noble";
}
}
// Instantiate Book object
const book1 = new Book("The Old Man and the Sea", "Earnest Hemingway", "1952");
console.log(Book.topBookStore());
Subclasses
class Lexicon extends Book {
constructor(title, author, year, partNumber) {
super(title, author, year);
this.partNumber = partNumber;
}
}
// Instantiate Lexicon object
const lex = new Lexicon("Mammals", "Charles Darwin", "1940", "3");
console.log(lex.getSummary());
Class File
class Duck extends Bird {
constructor(name, size, isAbleToSwim, isAbleToFly, quack) {
super(name, size, isAbleToSwim, isAbleToFly);
this.quack = quack;
}
}
export default Duck;
Setters and getters
class BirdsNest {
set eggsCount(numberOfEggs) {
}
get eggsCount() {
}
}
Destructuring
const [a, b, ...c] = [5,10,15,20];
let [a, b] = [1,2];
let {a, b, ...c} = {a: 10, b: 20, c: 30, d: 40};
({a, b} = {a: 10, b: 20});
const data = { foo: 45, bar: 23, name: 'Poppy' };
// subset
const { name, ...rest } = data;
console.log(rest) // { foo: 45, bar: 23 }
// renaming
const { name: firstName, foo: age };
console.log(firstName, age) // "Poppy", 45
// defaults
const { len: length = 0 } = {};
console.log(length) // 0
JSON
JSON.parse(jsonString)
JSON.stringify(object)
Errors
try {
dangerousCall()
} catch(error) {
console.log(error)
}
try {
if (x == "") throw "empty"
if (isNan(x)) throw "not a number"
x = Number(x)
} catch(error) {
console.error(error)
} finally {
console.log("done")
}
ES6 JavaScript Modules
<script type="module" src="main.js"></script>
Named Export
* `var`
* `let`
* `const`
* `function`
* `class`
```js
export const name = 'apple';
export function drawApple() { … }
export at the end of a file
export { name, drawApple };
export {
function1 as firstFunction,
function2 as secondFunction
};
Named Import
import { name, drawApple } from './modules/apple.js';
import {drawApple as createApple} from './modules/apple.js';
Default Export
export default peachName;
export default function(context) { … }
Import Default
import drawPeach from './modules/peach.js';
Namespacing
import * as Module from './modules/module.js';
Module.function1()
Module.function2()
JSON Module script
import data from "./data.json" with { type: "json" };
console.log(data);
Dynamic Module Loading
import('./modules/myModule.js')
.then((Module) => {
// Do something with the module.
const square = new Module.Square(canvas.context)
square.draw();
});