HTML 5 Elements
DOM
- Document Object Model
- Provides structural representation for HTML (and XML) documents
- The DOM represents all of the different elements and their relationship to each other
- Elements nested inside others have a parent and child relationship while elements that share the same parent have a sibling relationship.
Parsing HTML
Elements, tags and attributes
<a href="#" target="_blank">I'm a link</a>
Comments
<!-- this is a comment -->
Inline Event Listener
<div onclick="var event = arguments[0] || window.event; [...]"></div>
<span onclick="event.stopPropagation(); alert('you clicked inside the header');">something inside the header</span>
Document structure
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- -->
</body>
</html>
Head
Language
langglobal attribute
<html lang="en">
</html>
Adding CSS to HTML
Options
- include external file in header (preferred!)
- internal styles in header
- inline via the
styleattribute
<link rel="stylesheet" href="main.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="subfolder/main.css">
Adding JavaScript to HTML
Best place
- right before
</body>tag (after all of the HTML has been parsed) - inside
<head>, if JavaScript is needed to help render HTML and determine it’s behavior
<script src="script.js"></script>
Meta
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<meta name="description" content="Description ...">
For details see Meta Tags.
Scripts
Attributes
async: no guarantee which file withasyncattribute loads first
<script async src="external-js.js"></script>
<script async src="other-external-js.js"></script>
defer: would not run until the page was ready- execute in order, but still not block the rest of the page while the files are being downloaded to the browser. Usecase: a script that needs to synchronize with any other script, i.e. load before or after
<script defer src="external-js.js"></script>
<script defer src="other-external-js.js"></script>
Event Listeners in HTML
Simple Script that is runw when the HTML finished loading
<body onload="init();">
<!-- all the HTML content ... -->
<script>
function init() {
document.body.innerHTML = "HTML Loaded";
}
</script>
</body>
*/
Anchor link
inline-level (may wrap block-level elements)
<a href="https://apple.com">Apple</a>
Paths
- relative path: "pages/about.html"
- absolute path: "/pages/about.html"
URL Hash & query string
#id?query=123&query2=abc
URL text fragments
:~:text=[prefix-,]textStart[,textEnd][,-suffix]#:~:text=<first word>,<last word>example.com#:~:text=foo&text=bar&text=bazWICG | scroll to text fragment
Style with CSS via :target selector
Linking to an email adress
<a href="mailto:markusdoppler@me.com">Email me</a>
adding a predefined email
<a href="mailto:markusdoppler@me.com?subject=Email%20subject&body=How%20are%20you">Email me</a>
- The first parameter following the email address must begin with a question mark
? - binding one parameter to another we need to use the ampersand
&to separate the two. - spaces are encoded with
%20 - line-breaks are encoded with
%0A
Directly downloading a file via download attribute
<a href="image.png" class="btn btn-primary" download>Download Image</a>
Opening Links in a New Window
<a href="https://apple.com">apple</a>
open in the same window (default)
<a href="https://apple.com" target="_self"></a>
open in a new window / tab
<a href="https://apple.com" target="_blank"></a>
Linking to Parts of the Same Page
- set an
idattribute on the element we wish to link to
<h2 id="section-3">
- Create a link to that element
<a href="#section-3">go to section 3</a>
<!-- Indicates that the current document's original author or publisher does not endorse the referenced document -->
<a href="" rel="nofollow">
rel value |
Description | <link> |
<a> and <area> |
<form> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
alternate |
Alternate representations of the current document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | – |
author |
Author of the current document or article. | 🔗 | 🔗 | – |
bookmark |
Permalink for the nearest ancestor section. | – | 🔗 | – |
canonical |
Preferred URL for the current document. | 🔗 | – | – |
dns-prefetch |
Tells the browser to preemptively perform DNS resolution for the target resource's origin. | 🚪 | – | – |
external |
The referenced document is not part of the same site as the current document. | – | Annotation | Annotation |
help |
Link to context-sensitive help. | 🔗 | 🔗 | 🔗 |
icon |
An icon representing the current document. | 🚪 | – | – |
license |
Indicates that the main content of the current document is covered by the copyright license described by the referenced document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | 🔗 |
manifest |
Web app manifest. | 🔗 | – | – |
me |
Indicates that the current document represents the person who owns the linked content. | 🔗 | 🔗 | – |
modulepreload |
Tells to browser to preemptively fetch the script and store it in the document's module map for later evaluation. Optionally, the module's dependencies can be fetched as well. | 🚪 | – | – |
next |
Indicates that the current document is a part of a series and that the next document in the series is the referenced document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | 🔗 |
nofollow |
Indicates that the current document's original author or publisher does not endorse the referenced document. | – | ✍️ | ✍️ |
noopener |
Creates a top-level browsing context that is not an auxiliary browsing context if the hyperlink would create either of those, to begin with (i.e., has an appropriate target attribute value). | – | ✍️ | ✍️ |
noreferrer |
No Referer header will be included. Additionally, has the same effect as noopener. | – | ✍️ | ✍️ |
opener |
Creates an auxiliary browsing context if the hyperlink would otherwise create a top-level browsing context that is not an auxiliary browsing context (i.e., has "_blank" as target attribute value). | – | ✍️ | ✍️ |
pingback |
Gives the address of the pingback server that handles pingbacks to the current document. | 🚪 | – | – |
preconnect |
Specifies that the user agent should preemptively connect to the target resource's origin. | 🚪 | – | – |
prefetch |
Specifies that the user agent should preemptively fetch and cache the target resource as it is likely to be required for a followup navigation. | 🚪 | – | – |
preload |
Specifies that the user agent must preemptively fetch and cache the target resource for current navigation according to the potential destination given by the as attribute (and the priority associated with the corresponding destination). | 🚪 | – | – |
prerender |
Specifies that the user agent should preemptively fetch the target resource and process it in a way that helps deliver a faster response in the future. | 🚪 | – | – |
prev |
Indicates that the current document is a part of a series and that the previous document in the series is the referenced document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | 🔗 |
privacy-policy |
Gives a link to a information about the data collection and usage practices that apply to the current document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | – |
search |
Gives a link to a resource that can be used to search through the current document and its related pages. | 🔗 | 🔗 | 🔗 |
stylesheet |
Imports a style sheet. | 🚪 | – | – |
tag |
Gives a tag (identified by the given address) that applies to the current document. | – | 🔗 | – |
terms-of-service |
Link to the agreement, or terms of service, between the document's provider and users who wish to use the document. | 🔗 | 🔗 | – |
– Not allowed 🔗 Link 🚪 External Resource ✍️ Annotation
Text
Headings
block-level elements
<h1>1 Heading</h1>
<h2>1.2 Heading</h2>
<h3>1.2.3 Heading</h3>
<h4>1.2.3.4 Heading</h4>
<h5>1.2.3.4.5 Heading</h5>
<h6>1.2.3.4.5.6 Heading</h6>
Paragraphs
block-level elements
<p></p>
Bold text
inline-level elements
strong importance
<strong></strong>
stylistically offset text
<b></b>
Italic text
inline-level elements
stressed emphasis
<em></em>
Alternative voice or tone (almost as if it were placed in quotation marks)
<i></i>
Small text
inline-level element
<small></small>
- USES: copyright information
Citations & Quotes
<cite> is used to reference a creative work, author, or resource
<q> is used for short, inline quotations
<q cite="https://markusdoppler.at">
<blockquote> is used for longer external quotations
<blockquote cite="https://markusdoppler.at">
Summary and Details
<details>
<summary>Summary</summary>
<p>Details....</p>
</details>
Encoding Special Characters
| encoding | symbol |
|---|---|
– |
– |
­ |
(line-break possibility) |
© |
© |
é |
é |
— |
— |
“ |
“ |
” |
” |
’ |
’ |
< |
< |
> |
> |
& |
& |
Time
<time datetime="08:30:00">8:30 AM</time>
Divisions and Spans
- Container elements (for styling)
Divisions
block-level element
<div></div>
Span
inline-level element
<span></span>
Images, Audio and Video
Images
inline-level element
<img src="broccoli.png" alt="Broccoli">
<img src="https://markusdoppler.at/broccoli.png" alt="Broccoli!">
Attributes
src: source of the image- most commonly supported: gif, jpg, and png
- jpg images used for photographs (high colour count, low file size)
- png images used for icons or background patterns (transparencies)
alt: alternative text for search engines and assistive technologieswidthandheight: to tell the browser how large the image should be before the page even loads - faster page rendering! (attention: CSSwidthandheightattributes will take precedence over the HTML attributes)
Audio (HTML5)
block-level element
<audio src="jazz.mp3"></audio>
<audio controls>
<source src="jazz.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
<source src="jazz.mp3" type="audio/mp3">
<source src="jazz.wav" type="audio/way">
Fallback (e.g. download link) if browser does not support audio element
</audio>
Attributes
src: most commonly supported: ogg, mp3, and wavcontrols: will display a browser’s default audio controls, including play and pause, seek, and volume controls, by default nothing will be displayedautoplay: audio will automatically play upon loadingloop: will cause an audio file to repeat continually, from beginning to endpreload="none|auto|metadata"none: won’t preload any information about an audio fileauto(default): will preload all information about an audio filemetadata: will preload any available metadata information about an audio file, such as the clip’s length, but not all information
Video (HTML5)
block-level element
<video src="clip.mov"></video>
<video controls poster="earth-video-screenshot.jpg">
<source src="clip.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="clip.ogv" type="video/ogg">
<source src="clip.mov" type="video/mov">
Fallback (e.g. download link) if browser does not support video element
</video>
Attributes
src: most commonly supported: mp4controls: if not specified, video will display by default; Best practise: always include, except if there is a reason not to allow users to start, stop, or replay the videoautoplay: video will automatically play upon loadingloopwidthandheight: better specify in CSSpreload="none|auto|metadata"poster: specify image to use as a poster image
A customized player can be implemented using JavaScript.
Inline Frame (HTML5)
block-level element
<iframe src="https://markusdoppler.at"></iframe>
Attributes
frameborderwidthandheight
Figure
<figure>
<img src="dog.jpg">
<figcaption>a black, brown, and white dog</figcaption>
</figure>
Lists
Unordered Lists
block-level element
<ul>
<li>Orange</li>
<li>Green</li>
<li>Blue</li>
</ul>
Ordered Lists
block-level element
<ol start="5" reversed>
<li>Five</li>
<li value="66">Six</li>
<li>Seven</li>
</ol>
<ol> attributes
startreversed
<li> attributes
value
Nota Bene
- the only element we can place as a direct child of the
<ul>and<ol>elements is the<li>element - the
<li>element has to be a direct child of either a<ul>or<ol>element
Description Lists
block-level element
<dl>
<dt>physics</dt>
<dd>the branch of science concerned with the nature and properties of matter and energy</dd>
<dt>biology</dt>
<dd>the study of living organisms</dd>
</dl>
Nested lists
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li>
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
Forms
Form
<form action="/login" method="post">
...
</form>
Attributes
action: contains the URL to which information included within the form will be sent for processing by the servermethod: HTTP method browsers should use to submit the form data
Attributes for all form elements
disabled: turns off an element or control so that it is not available for interaction or inputplaceholder(HTML5): provides a hint or tip within the form control of an<input>or<textarea>element that disappears once the control is clicked in or gains focusvalue: value text stays in place when a control has focus unless a user manually deletes it; use case: pre-populating datarequired(HTML5): enforces that an element or form control must contain a value upon being submitted to the server otheracceptautocompleteautofocusformactionformenctypeformmethodformnovalidateformtargetmaxmaxlengthminpatternreadonlyselectionDirectionstep
Text Fields
<input type="text" name="username">
Attributes
typetextpasswordcolor(the following are all new in HTML5)datedatetimeemailmonthnumberrangesearchteltimeurlweek
name
Text Areas
<textarea name="comment">Add your comment here</textarea>
Attributes
namecols: width in terms of the average character widthrows: number of lines of visible text- Best practise:
widthandheightusing CSS
Radio Buttons
Only one of the radio buttons of one group (denoted by name attribute) can be selected
<input type="radio" name="day" value="Friday" checked> Friday
<input type="radio" name="day" value="Saturday"> Saturday
<input type="radio" name="day" value="Sunday"> Sunday
Attributes
type=radioname: radio buttons with the samenameattribute value correspond to one anothervalue: specific value for radio buttonchecked(boolean): preselected radio button
Checkboxes
check boxes allow users to select multiple values and tie them all to one control name
<input type="checkbox" name="day" value="Friday" checked> Friday
<input type="checkbox" name="day" value="Saturday" checked> Saturday
<input type="checkbox" name="day" value="Sunday"> Sunday
Attributes
type=checkboxname: checkboxes with the samenameattribute value correspond to one anothervalue: specific value for checkboxchecked(boolean): a preselected checkbox
Drop-Down Lists
the perfect format for a long list of choices
<select name="day">
<option value="Friday" selected>Friday</option>
<option value="Saturday">Saturday</option>
<option value="Sunday">Sunday</option>
</select>
select Attributes
name: drop-down lists with the samenameattribute value correspond to one anothermultiple: choose more than one option from the list at a time (to choose multiple options one will need to hold down the Shift key while clicking to make selections)
option Attributes
value: specific value for an optionselected(boolean): a preselected option
Hidden Input
<input type="hidden" name="tracking-code" value="abc-123">
File Input
<input type="file" name="file">
Menu
<menu>
<button>A</button>
<button>B</button>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</menu>
Submit
Submit Input
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="send">
Attributes
value: is used to specify the text that appears within the button
Submit Button
default: performs the same way as the <input> element with the type attribute value of submit
<button name="submit">
Sumbit <i>Me</i>!
</button>
Attributes
value: is used to specify the text that appears within the button
Labels
<label for="username">Username</label>
<input type="text" name="username" id="username">
Attributes
for: matching up theforandidattribute values ties the two elements together
clicking the label associated with an input element brings it in focus
Nesting Label and Input
allows omission of the for and id attributes
<label>
Username
<input type="text" name="username">
</label>
Fieldset
block-level element
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
Legend
provides a caption, or heading, for the <fieldset> element
<legend>Billing address</legend>
Tables
Table
<table>
<tr>
<th scope="col">...</th>
<th scope="col">...</th>
<th scope="col">...</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>...</td>
<td>...</td>
<td>...</td>
</tr>
...
</table>
Table Row
<tr>
...
</tr>
Table Data
<td>...</td>
Attributes
headers: a cell, either a<td>or<th>element, needs to be associated with a different header, theheadersattribute comes into play. The value of the headers attribute on a<td>or<th>element needs to match theidattribute value of the<th>element that cell pertains to.colspan: span a single cell across multiple columns (default: 1)rowspan: span a single cell across multiple rows (default: 1)
Table Header
works just like the <td> element in that it creates a cell for data, but signifies that the data within the cell is a heading
may be used within both columns and rows
<th scope="col">...</th>
Attributes
scope: helps to identify exactly what content a table header relates tocolrowcolgrouprowgroup
colspan: span a single cell across multiple columns (default: 1)rowspan: span a single cell across multiple rows (default: 1)
Table Structure
Table Caption
provides a caption or title for a table
must come immediately after the opening <table> tag
<table>
<caption>...</caption>
...
</table>
Table Head, Body and Foot
<table>
<caption>...</caption>
<thead>
...
</thead>
<tbody>
...
</tbody>
<tfoot>
...
</tfoot>
</table>
Attributes
ID
id="section-2"
Class
class="broccoli"
class="broccoli green-veg"
Hidden
- semantically more correct than
display: none;in CSS.
<div hidden>....</div>
Inline Style
<h1 style="text-align: center">My Heading</h1>
src
<img src="">
<script src=""></script>
href
<a href=""></a>
<link href="" rel="">
Self-closing (Single) Elements
<br>
<embed>
<hr>
<img>
<input>
<link>
<meta>
<param>
<source>
<wbr>
Structurally Based Elements
block-level elements
<header>
<nav>
<article>
<section>
<aside>
<footer>
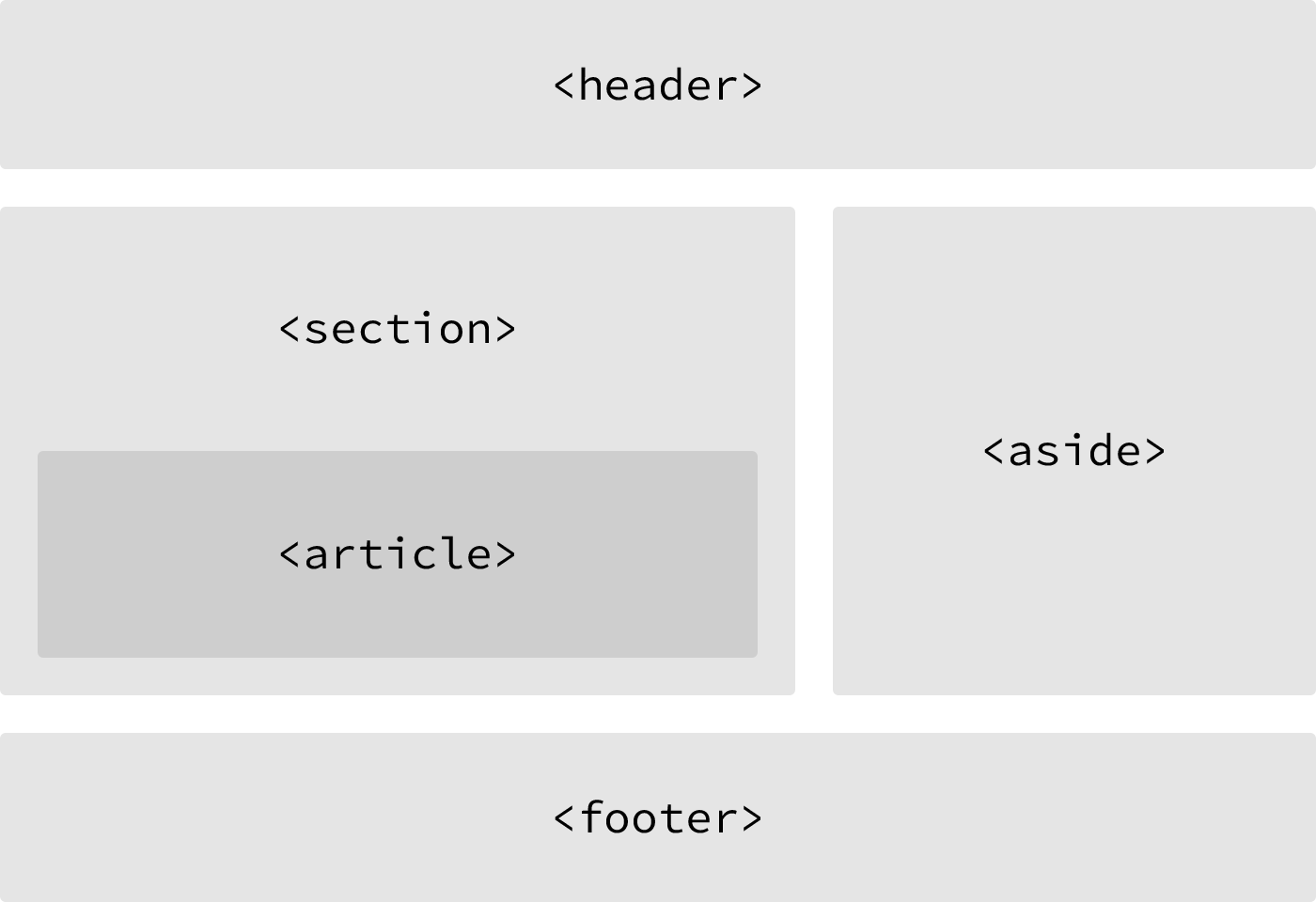
SEMANTICS & GOOD PRACTICES
<header>
may include a heading, introductory text, and even navigation
<nav>
global navigation, a table of contents, previous/next links, or other noteworthy groups of navigational links
may contain anchor elements with links to other pages within the same website or to parts of the same web page
<article>
content within the element could be replicated elsewhere without any confusion
content can be independently redistributed or syndicated
<section>
a thematic grouping of content, which generally, but not always, includes a heading
commonly used to break up and provide hierarchy to a page
<aside>
holds content, such as sidebars, inserts, or brief explanations
<footer>
identifies the closing or end of a page, article, section, or other segment of a page
Display Levels
Block-Level Elements
block-level elements
<div></div>
<h1></h1>
<h2></h2>
<h3></h3>
<h4></h4>
<h5></h5>
<h6></h6>
Inline-Level Elements
inline-level elements
<span></span>
Other elements
<br><hr><base><sub><sup><meta>
Custom Tags and Attributes
<my-book data-pages="400" data-author="Nietzsche">The Wanderer and His Shadow</my-book>
var myBook = document.createElement('my-book');
myBook.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
alert('Thanks!');
});
Use the new operator:
var myBook = new myBook();
document.body.appendChild(myBook);
- Hyphenation! Custom elements should consist of at least one - like my-book or app-menu or header-title etc. Just, don't use
data-*since it's reserved for data-attributes. - All custom elements have a display of
inlineby default. You can change that with CSS or JavaScript, however. - Internet Explorer does not recognize any of these elements unless you first "create" them with JavaScript:
document.createElement('my-book');
Drag and Drop API
<img>and<a>elements are draggable by default- other elements
<div draggable="true"></div>
.not-draggable {
-webkit-user-drag: none;
}